Anatomical models in the European context
Introduction to anatomical models
Human anatomy has fascinated scientists, artists and medical students for centuries. With the help of anatomical models, it is possible to better understand the structure of the human body. These models, often in the form of physical replicas, help in teaching, research and as a visualization tool. In the European context, anatomical models have a long history that dates back to the Renaissance, when people began to take an interest in accurate representations of the human body.
The evolution of anatomical models throughout history
The first anatomical models were created from clay, wood or wax, and over time they began to be produced from more durable materials, such as resin or metal. In the case of Europe, many of these models had their roots in the work of well-known anatomists such as Andreas Vesalius, who in the 16th century broke the clinical approach to anatomy with more accurate descriptions and illustrations.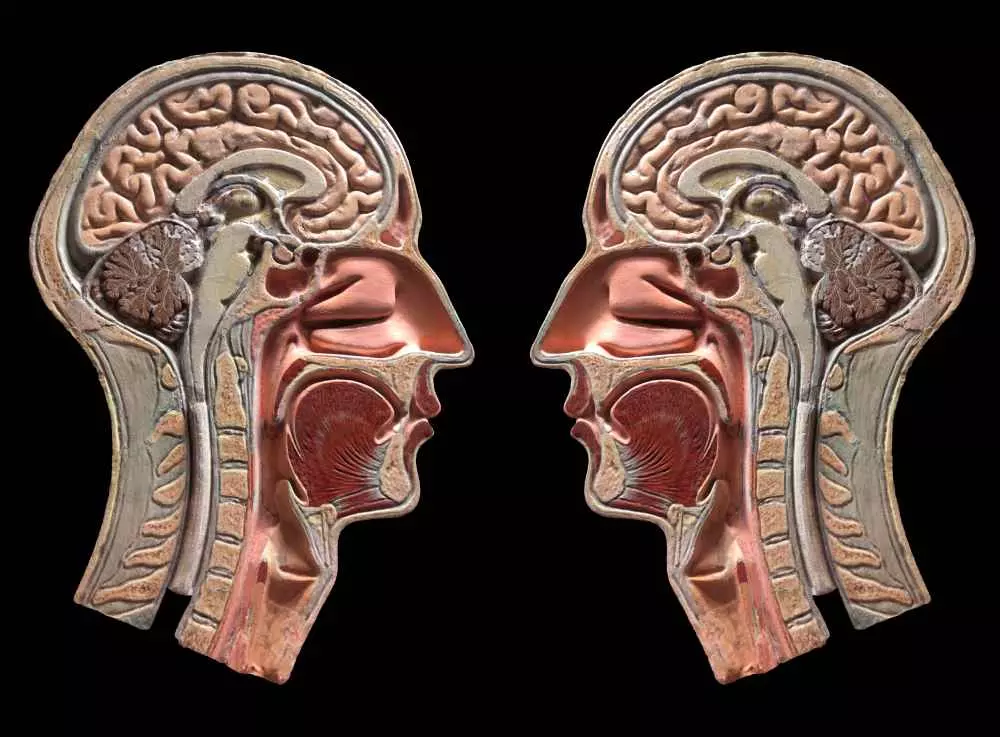
With evolving technology, these models have become increasingly realistic. The use of 3D printing in the 21st century has made it possible to create extremely detailed representations of individual anatomical structures, revolutionizing medical education and scientific research.
Anatomical models in medical education
In medical education, anatomical models play a key role. They allow students to learn about different parts of the body, and their functions, in practice. They are used in practical classes and lectures, where they can visually analyze the complexity of the structure of the human body.
Examples of models include skeletal models, detailed replicas of organs, and full-face anatomical models that capture the appearance and proportions of the human body. They enable students to understand the topography of organs and their interrelationships.
The role of anatomical models in medical research
In the context of medical research, anatomical models are irreplaceable. They allow researchers to accurately represent anatomical cases and develop new surgical procedures. With them, operations can be simulated and potential problems can be anticipated, which is invaluable in surgery.
In addition, models can be used in biomedical research, where anatomical simulations help scientists better understand pathology. It is worth noting that progressive virtualization and computer modeling are becoming more common, enabling remote research and greater interactivity in teaching.
Anatomical models in culture and art
Not only in medicine, but also in the arts, anatomical models find their use. As early as the Renaissance, artists such as Leonardo da Vinci drew inspiration from anatomy, creating works full of detail and realism. Modern models allow artists to approach the subject of the human body in innovative ways.
In European galleries and museums, you can find anatomical models that not only serve an educational function, but are also works of art. Contemporary exhibitions often combine science with artistic interpretations of anatomy, which makes the subject of anatomy even more fascinating.
Challenging anatomical models
As in any field, there are challenges in the area of anatomical models as well. A major issue is maintaining ethics in the reproduction of human structures. It is important that the models created comply with current scientific knowledge and ethical standards. It is also necessary to regulate the use of anatomical models in education and research.
In addition, the development of 3D technology poses intellectual property protection and licensing challenges for model manufacturers. It is important to indicate what, when interacting with the models, students and researchers should observe.
The future of anatomical models in Europe
From the perspective of the future, anatomical models in Europe are bound to grow. With advances in technology, such as virtual reality and artificial intelligence, new ways of learning and research that have the potential to change paradigms in medical education are becoming possible.
Thanks to globalization and collaboration between different research centers in Europe, the quality of anatomical models will only increase, and their use will become even more widespread. These models will play a key role in the development of |medicine and in further unraveling the mysteries of the human body.
Summary
Anatomical models are a powerful tool in education, research and the arts that are gaining importance in the European context. Their evolution, use and future show how important they are in our understanding of the human body. The use of modern technology, such as 3D printing, opens new horizons for science and the joy of rediscovering the mysteries of our anatomy.